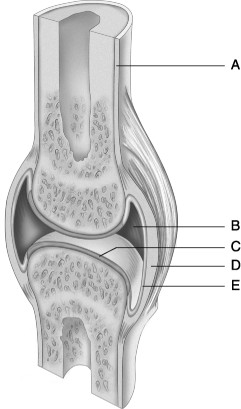
Figure 8.1
Using Figure 8.1, match the following:
Chapter 8, Anatomy and Physiology, Mr. Mazzulli
Please Do Not Write on This Test.
| SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. | ||
 Figure 8.1 Using Figure 8.1, match the following: | ||
| 1) | Periosteum. | 1) ______ |
| 2) | Articular cartilage. | 2) ______ |
| 3) | Joint (synovial) cavity. | 3) ______ |
| 4) | Synovial membrane. | 4) ______ |
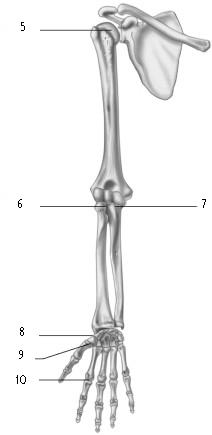 Figure 8.2 Using Figure 8.2, what type of axis does each joint have? A. Nonaxial B. Uniaxial C. Biaxial D. Multiaxial | ||
| 5) | ________ | 5) ______ |
| 6) | ________ | 6) ______ |
| 7) | ________ | 7) ______ |
| 8) | ________ | 8) ______ |
| 9) | ________ | 9) ______ |
| 10) | ________ | 10) ______ |
| TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. | ||
| 11) | Hinge joints permit movement in only two planes. | 11) ______ |
| 12) | The major role of ligaments at synovial joints is to help direct movement and restrict undesirable movement. | 12) ______ |
| 13) | The only movement allowed between the first two cervical vertebrae is flexion. | 13) ______ |
| 14) | Movement at the hip joint does not have as wide a range of motion as at the shoulder joint. | 14) ______ |
| 15) | The wrist joint can exhibit adduction and eversion movements. | 15) ______ |
| 16) | Moving the arm in a full circle is an example of circumduction. | 16) ______ |
| 17) | Flexion of the ankle so that the superior aspect of the foot approaches the shin is called dorsiflexion. | 17) ______ |
| 18) | A ball-and-socket joint is a multiaxial joint. | 18) ______ |
| 19) | Bending of the tip of the finger exhibits flexion. | 19) ______ |
| MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. | ||
| 20) | A fibrous joint that is a peg-in-socket is called a ________ joint. | 20) ______ |
| A) gomphosis | |
| B) synchondrosis | |
| C) syndesmosis | |
| D) suture |
| 21) | An immovable joint found only between skull bones is called a ________. | 21) ______ |
| A) condyle | |
| B) cartilaginous joint | |
| C) suture | |
| D) synovial joint |
| 22) | A joint united by dense fibrocartilaginous tissue that usually permits a slight degree of movement is a ________. | 22) ______ |
| A) gomphosis | |
| B) suture | |
| C) syndesmosis | |
| D) symphysis |
| 23) | Connective tissue sacs lined with synovial membranes that act as cushions in places where friction develops are called ________. | 23) ______ |
| A) ligaments | |
| B) tendons | |
| C) bursae | |
| D) menisci |
| 24) | Articulations permitting only slight degrees of movement are ________. | 24) ______ |
| A) synovial joints | |
| B) synarthroses | |
| C) diarthroses | |
| D) amphiarthroses |
| 25) | Which of these joint types affords uniaxial movement? | 25) ______ |
| A) gliding | |
| B) hinge | |
| C) pivot | |
| D) ball and socket |
| 26) | ________ are cartilaginous joints. | 26) ______ |
| A) Gomphoses | |
| B) Sutures | |
| C) Syndesmoses | |
| D) Synchondroses |
| 27) | The gliding motion of the wrist is accomplished because of the ________ joint. | 27) ______ |
| A) condyloid | |
| B) hinge | |
| C) pivot | |
| D) plane |
| 28) | The ligaments that protect the alignment of the femoral and tibial condyles and limit the movement of the femur anteriorly and posteriorly are called ________. | 28) ______ |
| A) patellar ligaments | |
| B) cruciate ligaments | |
| C) anterior ligaments | |
| D) tibial collateral ligaments |
| 29) | Bending your head back until it hurts is an example of ________. | 29) ______ |
| A) flexion | |
| B) hyperextension | |
| C) circumduction | |
| D) extension |
| 30) | In the classification of joints, which of the following is true? | 30) ______ |
| A) All synovial joints are freely movable. | |
| B) Synarthrotic joints are slightly movable. | |
| C) In cartilaginous joints, a joint cavity is present. | |
| D) Immovable joints are called amphiarthroses. |
| 31) | A joint that is known as a suture is found ________. | 31) ______ |
| A) where functionally it is amphiarthrotic | |
| B) in areas where bones have not yet closed | |
| C) in areas most prone to fracture | |
| D) in the skull only |
| 32) | Fibrous joints are classified as ________. | 32) ______ |
| A) pivot, hinge, and ball and socket | |
| B) sutures, syndesmoses, and gomphoses | |
| C) symphysis, sacroiliac, and articular | |
| D) hinge, saddle, and ellipsoidal |
| 33) | In symphysis joints the articular surfaces of the bones are covered with ________. | 33) ______ |
| A) synovial membranes | |
| B) hyaline cartilage | |
| C) tendon sheaths | |
| D) fibrocartilage |
| 34) | Menisci refer to ________. | 34) ______ |
| A) tendon sheaths | |
| B) small sacs containing synovial fluid | |
| C) cavities lined with cartilage | |
| D) semilunar cartilage pads |
| 35) | Football players often sustain lateral blows to the extended knee. Which of the ligaments is/are damaged as a result? | 35) ______ |
| A) arcuate popliteal and the posterior cruciate | |
| B) suprapatellar | |
| C) oblique popliteal and extracapsular ligament | |
| D) medial collateral, medial meniscus, and anterior cruciate |
| 36) | Which of the following conditions is generally considered a noninflammatory type of arthritis? | 36) ______ |
| A) tendonitis | |
| B) rheumatoid arthritis | |
| C) osteoarthritis | |
| D) bursitis |
| 37) | Gouty arthritis is a painful condition caused by ________. | 37) ______ |
| A) excessive blood levels of uric acid deposited as crystals in the soft tissue joints | |
| B) a disorder in the body's immune system resulting in destruction of joints | |
| C) a bacterial infection in the bursae | |
| D) a thickening of the synovial membrane and a decrease in fluid production |
| 38) | When a ballerina points the toes, it is known as ________. | 38) ______ |
| A) circumduction | |
| B) protraction | |
| C) plantar flexion | |
| D) pronation |
| 39) | Extracapsular ligaments stabilizing the knee include ________. | 39) ______ |
| A) the patellar ligament extending from femur to patella | |
| B) the oblique popliteal crossing the knee anteriorly | |
| C) lateral and medial collateral ligaments preventing lateral or medial angular movements | |
| D) cruciate ligaments, which help secure the articulating bones together |
| 40) | Tendon sheaths ________. | 40) ______ |
| A) act as friction-reducing structures | |
| B) help anchor the tendon to the muscle | |
| C) form channels for tendons | |
| D) are lined with dense irregular connective tissue |